Installing Avi Vantage for VMware vCenter with NSX
Note: Starting with Avi Vantage 20.1.3, support for NSX-V full access is deprecated, and the support for NSX-V full access will be removed in the upcoming releases. It is recommended to:
- Migrate to Avi’s NSX-T integration
- In case NSX-V support is still required, it is recommended to configure Avi with a no-orchestrator cloud.
This guide is specific to NSX-V integration. To know more about how to deploy Avi Vantage in a vSphere environment with NSX-T managed networking and security, refer to the Avi Integration with NSX-T article.
Introduction
This guide describes how to install Avi Vantage into an vCenter environment with NSX network virtualization and security platform. The instructions in this guide can be used for installing Avi Vantage 17.1 and subsequent.
Avi Vantage is a software-based solution that provides real-time analytics as well as automated elastic application delivery services. Avi Vantage optimizes core web-site functions, including SSL termination and load balancing. Avi Vantage also provides access to network analytics, including end-to-end latency information for traffic between end-users and the load-balanced applications.
Avi Vantage can work over distributed virtual port groups belonging to both Distributed Virtual Switch (regular VLAN networks) and Logical Switch (VXLAN networks) as it is agnostic of underlying network infrastructure. Avi-NSX support is required only when the Distributed Firewall (DFW) is enabled (i.e. host prep is performed) on the cluster where Avi Vantage operates. This enables Avi to dynamically update the load balancing pool using NSX security groups and publish DFW rules to allow the load balancing control plane and data plane traffic.
If the Distributed firewall is not enabled on the vCenter clusters on which Avi Vantage operates, the NSX support feature is not required and should not be enabled. In this case installation and operation of Avi Vantage will follow regular VMware cloud with write/read access mode, as specified in Installing Avi Vantage for VMware vCenter).
Note: IPv6 is not supported for VMware vCenter as yet in Avi Vantage.
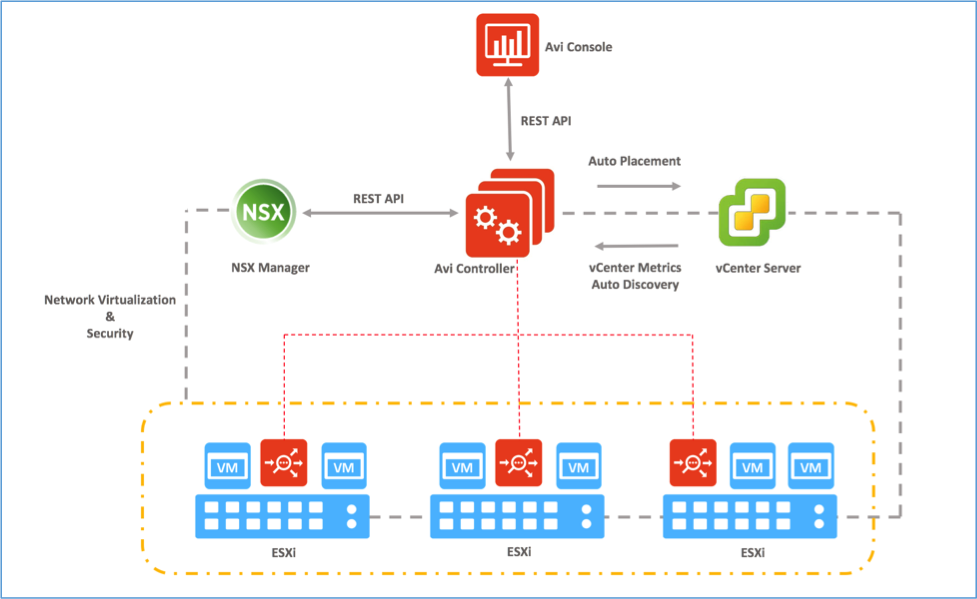
How Avi interacts with vCenter and NSX
Avi Vantage runs on virtual machines (VMs) managed by VMware vCenter. When deployed into a vCenter-managed VMware cloud, Avi Vantage performs as a fully distributed, virtualized system consisting of the Avi Controller and Avi Service Engines (Avi SEs), each running as a VM. Avi Controller also interacts with the NSX manager, using public REST APIs, to publish and manage rules to allow traffic between Avi infrastructure and the load balanced pool of VMs (control and data path traffic).
Avi Vantage is deployed and runs as the following main components:
- Avi Controller
- Avi Service Engines (Avi SEs)
Avi Controller
The Avi Controller provides a single point of control and management for the cloud. The Avi Controller runs on a VM and can be managed using its web interface, CLI, or REST API.
The Avi Controller stores and manages all policies related to services and management. Through vCenter, the Avi Controller discovers VMs, data centers, networks, and hosts. Through NSX manager, the Avi Controller discovers security groups and its members. Based on this auto-discovered information, virtual services can quickly be added using the web interface. To deploy a virtual service, the Avi Controller automatically selects an ESX server, spins up a Avi SE (described below), and connects it to the correct networks (port groups belonging to both distributed virtual switch and logical switch).
The Avi Controller can be deployed as a single VM or as a high availability cluster of three Avi Controller instances, each running on a separate VM.
Avi Service Engine
Avi SEs provide the application delivery services to end-user traffic, and collect real-time end-to-end metrics for traffic between end-users and applications.
Each Avi SE runs on its own VM. The Avi Controller manages the lifecycles of Avi SEs by creating, controlling, and deleting them. The Avi Controller creates a Avi SE VM, plumbs it into a network, provisions it with service policies as required to deploy virtual services and adds the Avi SE to exclusion list.
Interaction with Distributed Firewall
On the initial configuration of the cloud on Avi Vantage, it publishes DFW rule to allow management traffic between the Avi SEs and the Avi Controllers (see the Firewall Rules section of this article for more details). When virtual service is created, Avi Vantage publishes DFW rule to allow data path traffic (see Firewall Rules section for more details). All load balancing resources are constantly monitored by the Avi Controller and any changes are immediately updated on DFW rules and load balancing policies.
Installation Prerequisites
Software Requirements
The following table lists the software requirements.
| Component | Version |
|---|---|
| Avi Controller | Avi Vantage 17.1 and above |
| VMware vCenter | 5.5, 6.0, or 6.5 |
| NSX Manager | 6.2.4 and above |
NSX Requirements
Avi Vantage uses public APIs to interface with NSX Manager. For this Avi Vantage must use NSX Manager’s admin credentials.
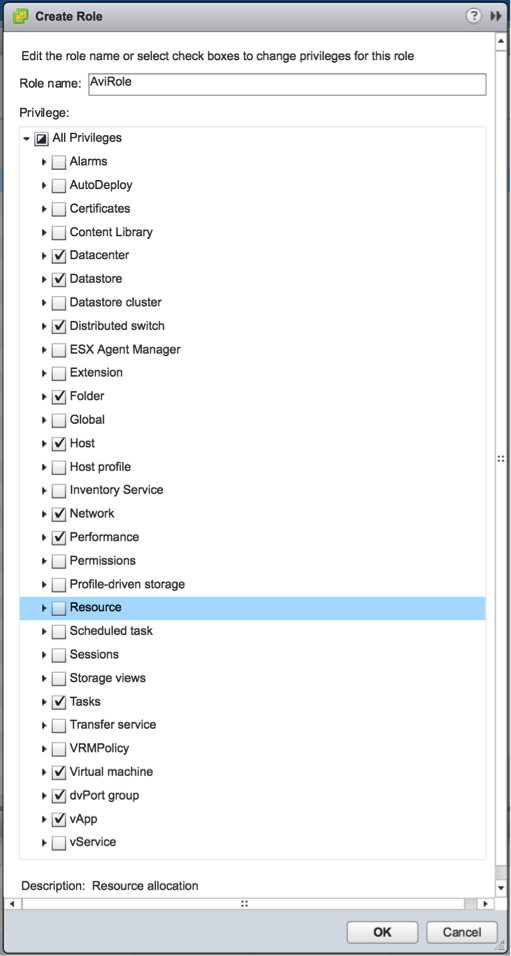
vCenter Account Requirement
During initial Avi Controller setup, a vCenter account must be entered to allow the Avi Controller to communicate with vCenter. The vCenter account must have privileges to create new folders in vCenter. This is required for the Avi SE creation, which in turn permits virtual service placement. The privileges required are depicted below.
Deploying the Avi Controller
From a vCenter client, log into the vCenter server. Using the vCenter client, deploy the Avi Controller OVA file.
- Click File on the top menu and choose Deploy OVF Template.
- Follow the instructions of the Deploy OVA Template wizard.
- Choose Thick Provision Lazy Zeroed for disk format.
- Choose a port group for Management access in Network Mapping. This port group will be used by the Avi Controller to communicate with vCenter.
- Specify the management IP address and default gateway. Or, leave them empty if using DHCP.
- Power on the VM.
Note: It is recommended to use a static IP address for the Avi Controller management interface, unless your DHCP server can keep the assigned IP address permanently.
Avi Controllers can be deployed as a single node. For production environments, it is recommended to deploy a three node Avi Controller cluster. Repeat above steps to deploy three instances of the Avi controller VMs, for production deployments.
Configuring Firewall Rules
Once the Avi Controller VMs are deployed, follow below steps to allow users access to the Avi Controller UI and CLI and allow Avi access to vCenter Infrastructure.
- On vCenter navigate to Networking and Security > Firewall
- Create a section called Avi-Access
- Create following rules in Avi-Access section:
| Name | Source | Destination | Services | Applied To |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avi-UI-CLI-Access | Any. User may set desired IPs to restrict access to Avi UI/CLI | Avi Controller VMs | SSH, HTTP, HTTPS | Avi Controller VMs |
| Avi-Infra-Access | Avi Controller VMs | IPSet/individual IPs of vCenter server, ESX hosts, NSX Manager | HTTPS | Avi Controller VMs. (see note below) |
| Avi-Cluster-Traffic | Avi Controller VMs | Avi Controller VMs | SSH, TCP 8443 | Avi Controller VMs |
Note: For the Avi-Infra-Access rule, add vCenter Server and NSX Manager to the Applied To field if they are deployed as a VM on hosts managed by same NSX Manager.
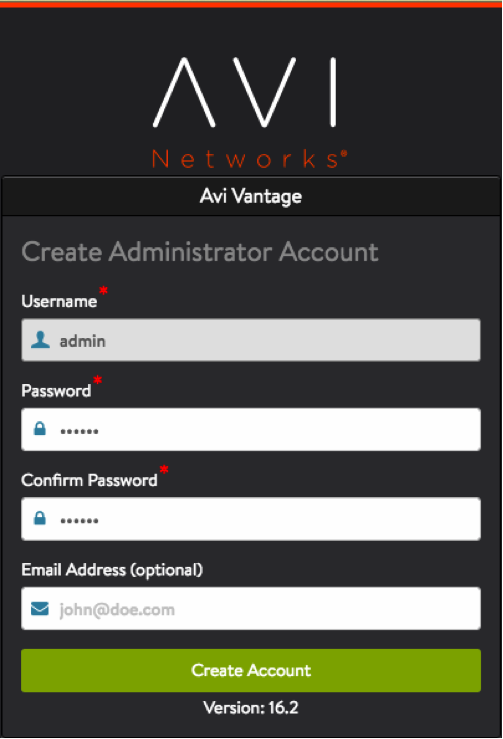
Perform Initial Setup of Avi Controller
This section shows how to perform initial configuration of the Avi Controller using its deployment wizard. In case of a clustered deployment, perform the below steps on only one of the Avi Controllers. The configuration is automatically synced to the other Avi Controllers when the cluster is configured.
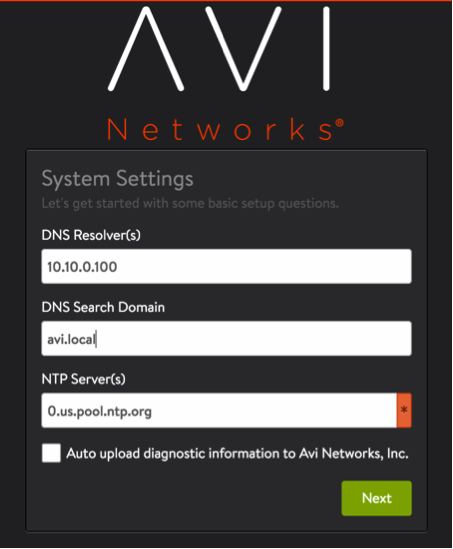
Access the Avi Controller UI from a browser and follow below six steps:
- Set a password for the admin user.
- Set DNS and NTP server information.
- Set email and SMTP information.
- Select No Orchestrator as infrastructure type.
- Click Next.
- Respond ‘No’ to the multiple tenants question.
Configuring Avi Controller Cluster
To configure the Avi Controller cluster, login to the first Avi Controller, configured in the previous section, and follow the steps below:
- Navigate to Administration > Controller > Nodes.
- Click Edit.
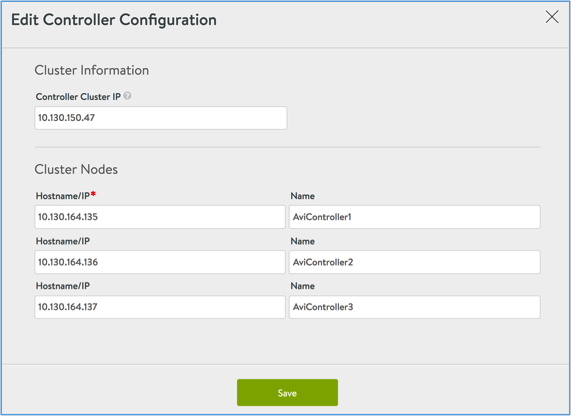
- The IP of the first Avi Controller will be present. Enter the IP addresses and names of the remaining two Avi Controllers.
- Assign a static IP as cluster IP.
- Click Save.
For more details, refer to the Deploying an Avi Controller Cluster article.
Configuring vCenter Cloud with NSX as SDN
Follow the steps below to configure the cloud:
- Navigate to Infrastructure > Clouds.
- Edit the Default-Cloud.
- Select VMware vCenter cloud and click Next.
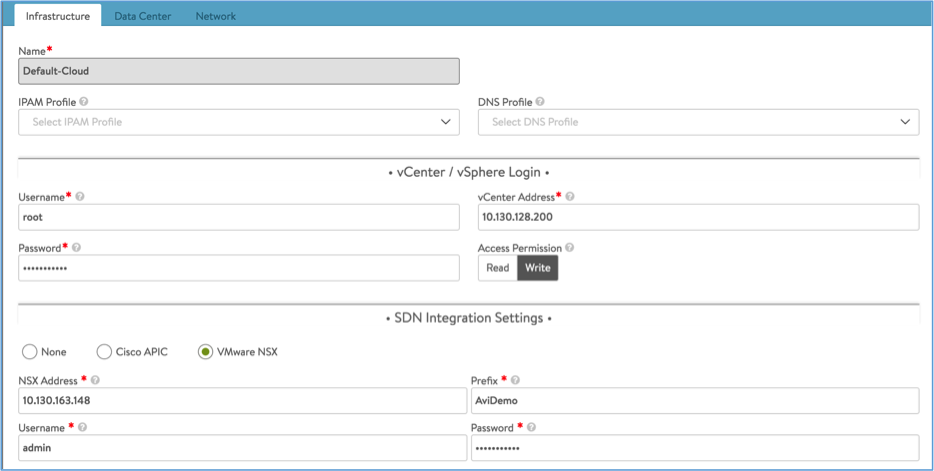
- On the Infrastructure tab,
- Enter vCenter credentials and IP address.
- Under SDN Integration, select the VMware NSX radio button.
- Enter the NSX Manager IP, user name, password and a desired prefix string. Note: The prefix string is used to identify NSX objects created by Avi Vantage.
- Click Next.
-
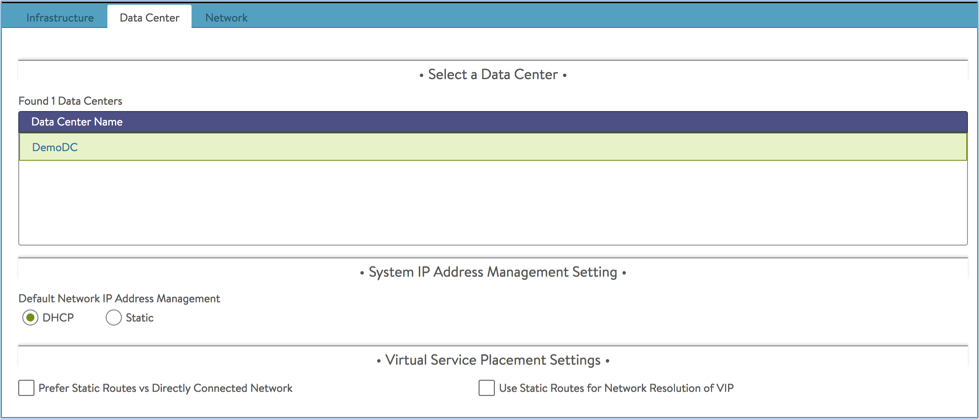
Select the data center and system IP address setting and click Next.
-
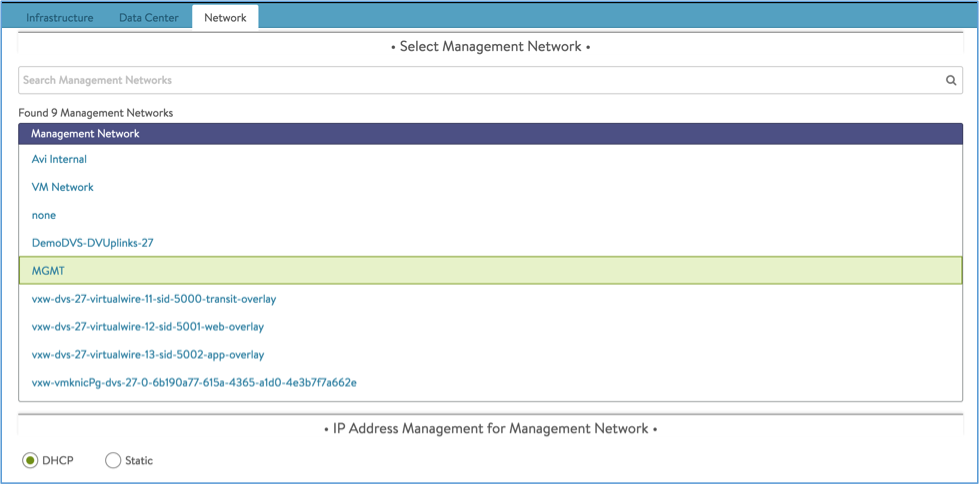
Select the management network and choose either DHCP or static IP address management for it.
-
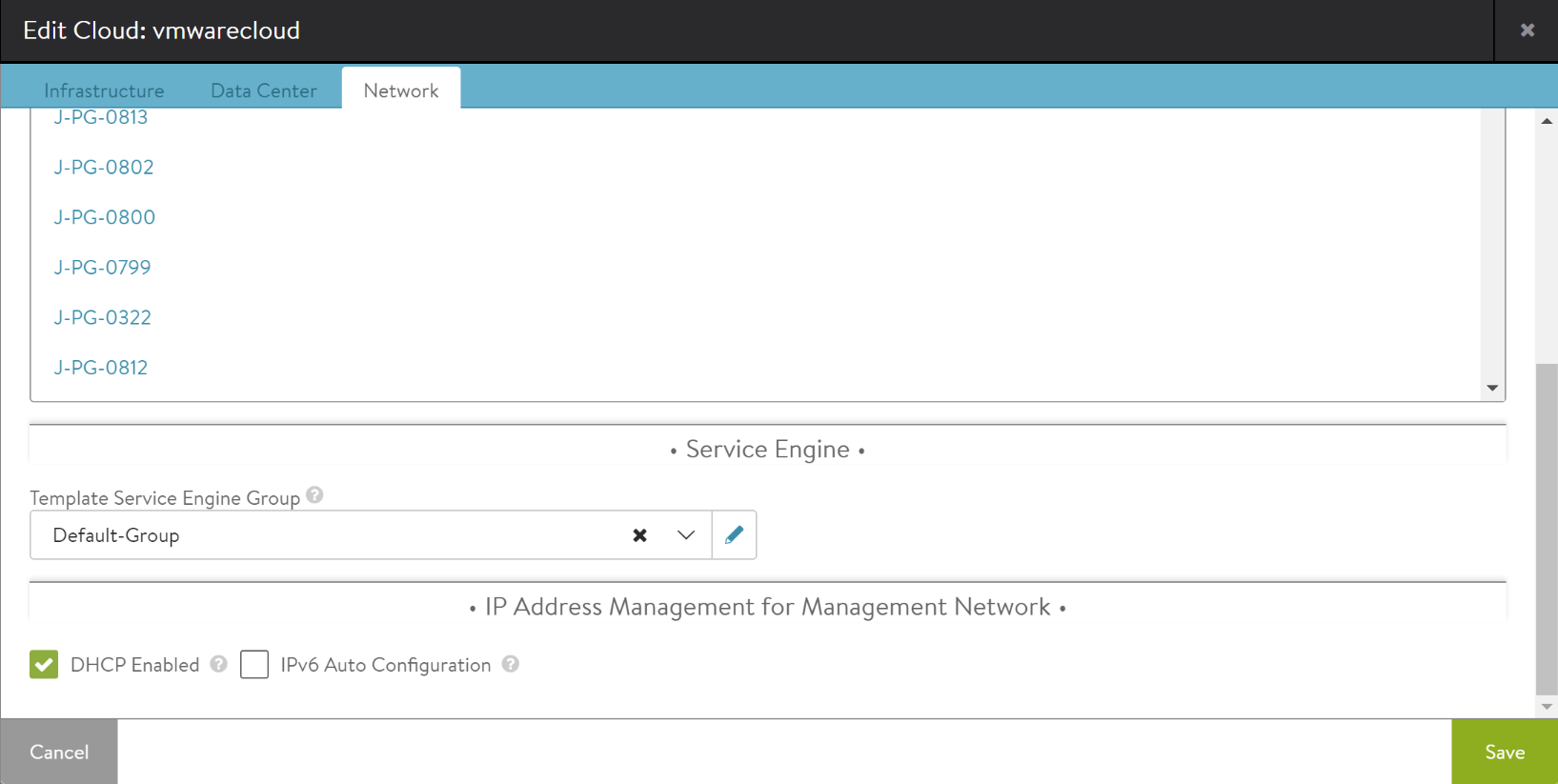
You can configure service engine by selecting the options from Template Service Engine Group field in Service Engine section.
- Click Save.
Firewall Rules
On configuring the cloud, the Avi Controller publishes a DFW section containing a rule to allow management traffic between the SE and the Avi Controller. For example, if the configured prefix is AviDemo, a section named AviDemo-Section is created.
The section is configured with a rule to allow management traffic from Avi SEs to the Avi Controller (Avi SEs initiate the secure connection with the Controller).
| Name | Source | Destination | Service | Applied To |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controller-SE-Rule | IPSet containing management IP addresses of all SEs | IPSet containing management IP addresses of all Avi Controllers in Controller cluster | Service containing TCP port 22 and 8443 | Distributed Firewall / Avi Controller VMs |
The IPSets are dynamically updated by the Avi Controller when Avi SEs are deployed or deleted. All SEs are automatically added to the exclusion list once they are deployed.
The applied-to field of the Controller-SE-Rule is set to Distributed Firewall by default, as the Controller can be installed outside the vSphere infrastructure managed by NSX. If the Avi Controller is deployed as a VM on an ESX managed by the same NSX Manager, the Avi Controller automatically detects this and sets the applied-to field to include all Avi Controller VMs.
Provisioning Load Balancing
NSX Security Groups
A security group is a collection of assets or grouping objects from your vSphere inventory. It may contain static members, such as VMs, vNICs, port groups, clusters, etc., or dynamic members, based on filter criteria with several parameters supported to match the search criteria. For more details on security groups refer to the VMware NSX document center. Using security groups, application developers can form a collection their server VMs which have same application running. This can be then used with the Distributed Firewall to collectively manage their security policies.
Create Back-end Server Security Group
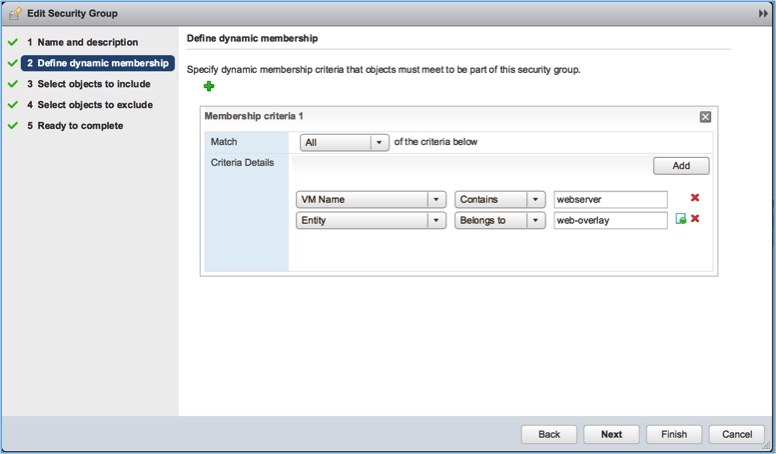
With NSX integration the user can add a pool of servers to a virtual service, in the form of an NSX security group. The security group is recommended to have dynamic membership based on VM name or VM security tag so that the servers can be dynamically added or removed from the load-balancing pool as they are created or destroyed. For example, the below figure shows AviDemo-web-sg security group defined to contain all VMs with “webserver” in the VM name with vNIC placed on “web-overlay.”
Note: Multiple dynamic criteria can be used to limit the security group resolution to only required IPs. E.g., in above case the server VMs have a management vNIC and a data vNIC. So the criteria ‘Entity - Belongs to – web-overlay’ helps select only the data vNICS placed on the web-overlay network.
Create Virtual Service
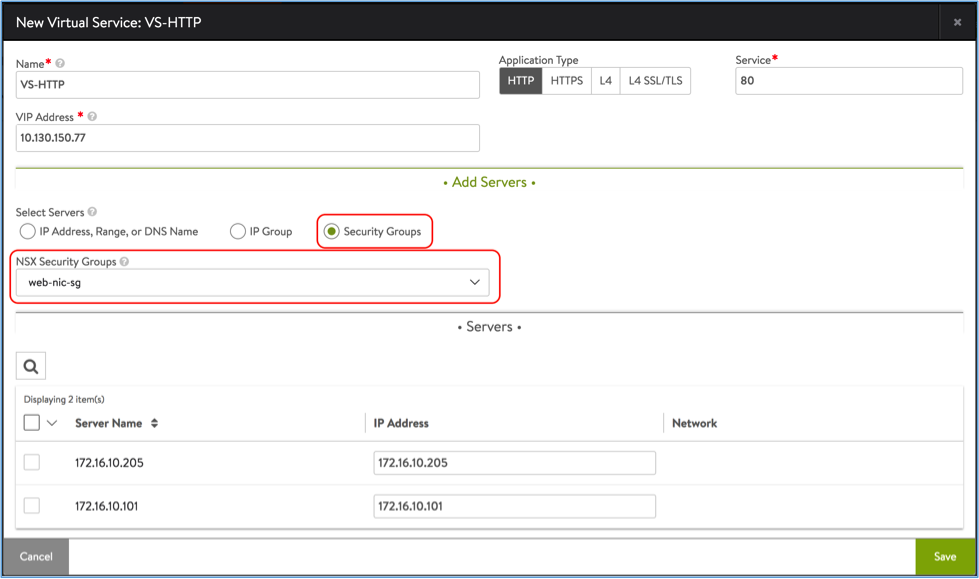
Creating a virtual service in setup with NSX integration is same as that with regular vCenter integration, with an exception that the pool needs to be configured using a NSX security group. Follow below steps to configure a basic HTTP virtual service:
- Log into the Avi Controller UI.
- Select Applications from the menu on the top left corner.
- Select Virtual Services on the top menu bar.
- Click Create Virtual Service -> Basic Setup.
- Enter a service name.
- Enter an IP address or DNS hostname for the virtual service.
- Click the Security Groups radio button.
- Select the back-end server security group from the dropdown.
- Click Save.
Note: Avi Vantage publishes and manages DFW rules only if the pool is configured using security group. User will have to manually provision the DFW rule if the pool is created using the IP Address Range or DNS Name, or IP Group option.
Firewall Rules
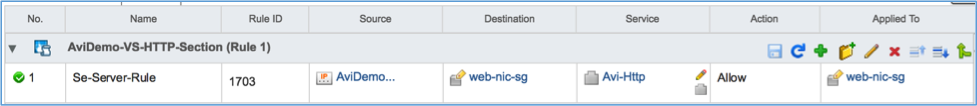
When a new virtual service is configured on the Avi Controller, a corresponding section is created on DFW (one section per virtual service). The section is named
The section is auto-configured according to the SE-Server-Rule rule:
| Name | Source | Destination | Service | Applied To |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE-Server-Rule | IPSet containing all data path IP addresses of SEs on which the VS is placed | Security group configured for pool on Avi Vantage | Service containing the protocol and port configured for the pool on Avi Vantage | Security group configured for pool on Avi Vantage |
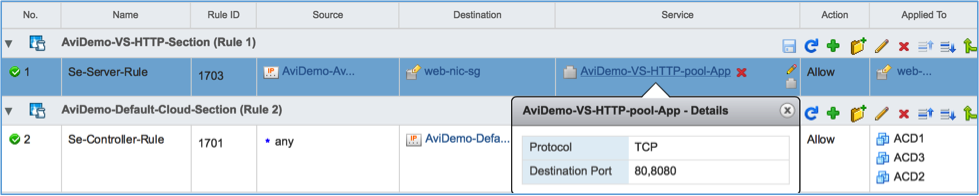
If the servers in the pool are configured with different ports, the Avi Controller creates a custom service object with the collection of configured ports and uses it as the service in the SE-Server-Rule. For example, if the pool has two servers configured with ports 80 and 8080, the rule will be:
All IPSets and services in these rules are dynamically updated by the Avi Controller when the VS or pool configuration is changed or the VS is scaled out/in.
Conclusion
This document showcased Avi Vantage and NSX interoperability in a vCenter environment. Avi Networks is completely integrated with VMware vCenter and fully qualified to work with NSX overlay and distributed routing technology. Avi Networks and VMware are working on a jointly eveloped API integration between NSX and Avi Vantage. This combination will enable users to configure Avi Vantage (virtual services, pools, etc.) dynamically, using the NSX Security Groups and auto-configure distributed firewall rules. This will enable IT organizations to fully leverage the combined strengths of NSX virtualization and automation with richer application delivery services enabled by Avi Vantage For more information on these solutions, please contact your Avi Networks representative.