VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer in Azure VMware Solution
Overview
About Azure VMware Solution (AVS)
Azure VMware Solution provides you with private clouds that contain vSphere clusters, built from dedicated bare-metal Azure infrastructure. The minimum initial deployment is three hosts, but additional hosts can be added up to a maximum of 16 hosts per cluster. All provisioned private clouds have vCenter Server, vSAN, vSphere, and NSX-T. You can migrate workloads from your on-premises environments, deploy new virtual machines (VMs), and consume Azure services from your private clouds. Azure VMware management tools (vCenter Server and NSX Manager) will be available at least 99.9% of the time. For more information, see the Azure VMware Solution page.
Azure VMware Solution is a VMware validated solution with on-going validation and testing of enhancements and upgrades. Microsoft manages and maintains private cloud infrastructure and software. It allows you to focus on developing and running workloads in your private clouds.
About NSX Advanced Load Balancer (NSX ALB)
VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer (NSX ALB, also known as Avi Vantage) is an enterprise grade, full featured load balancer, web application firewall and GSLB solution. Avi is a software based, distributed solution capable of providing application delivery features in both private and public cloud environments.
Network Services in AVS
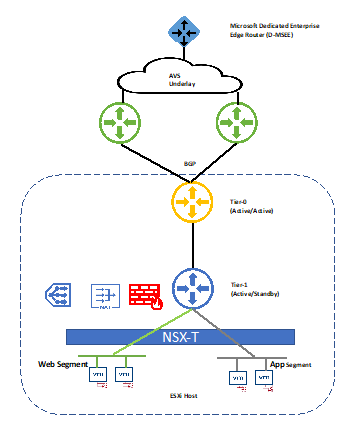
The following diagram demonstrates high-level network architecture of AVS Private Cloud VMware Network services:
From the diagram,
- AVS is pre-provisioned with the following NSX-T network configurations:
- Tier-0 Gateway configured in Active/Active mode for ECMP
- Northbound connectivity through BGP on Tier-0 Gateway
- Pre-provisioned Tier-1Gateway for workload segment connectivity
- Route advertisement enabled on pre-provisioned Tier-1 Gateway
- Route redistribution enabled on Tier-0 Gateway
- Default Internet Access for SDDC workloads with an option to enable/disable
- AVS allows customers to add the following NSX-T network configurations:
- Create overlay segments and connect workloads
- Deploy additional Tier-1 Gateways
- Deploy distributed services such as Distributed Fire Wall (DFW)
- Deploy stateful services such as Load Balancer, Gateway Firewall (GFW), DNS and DHCP on Tier-1 Gateway
Avi for AVS
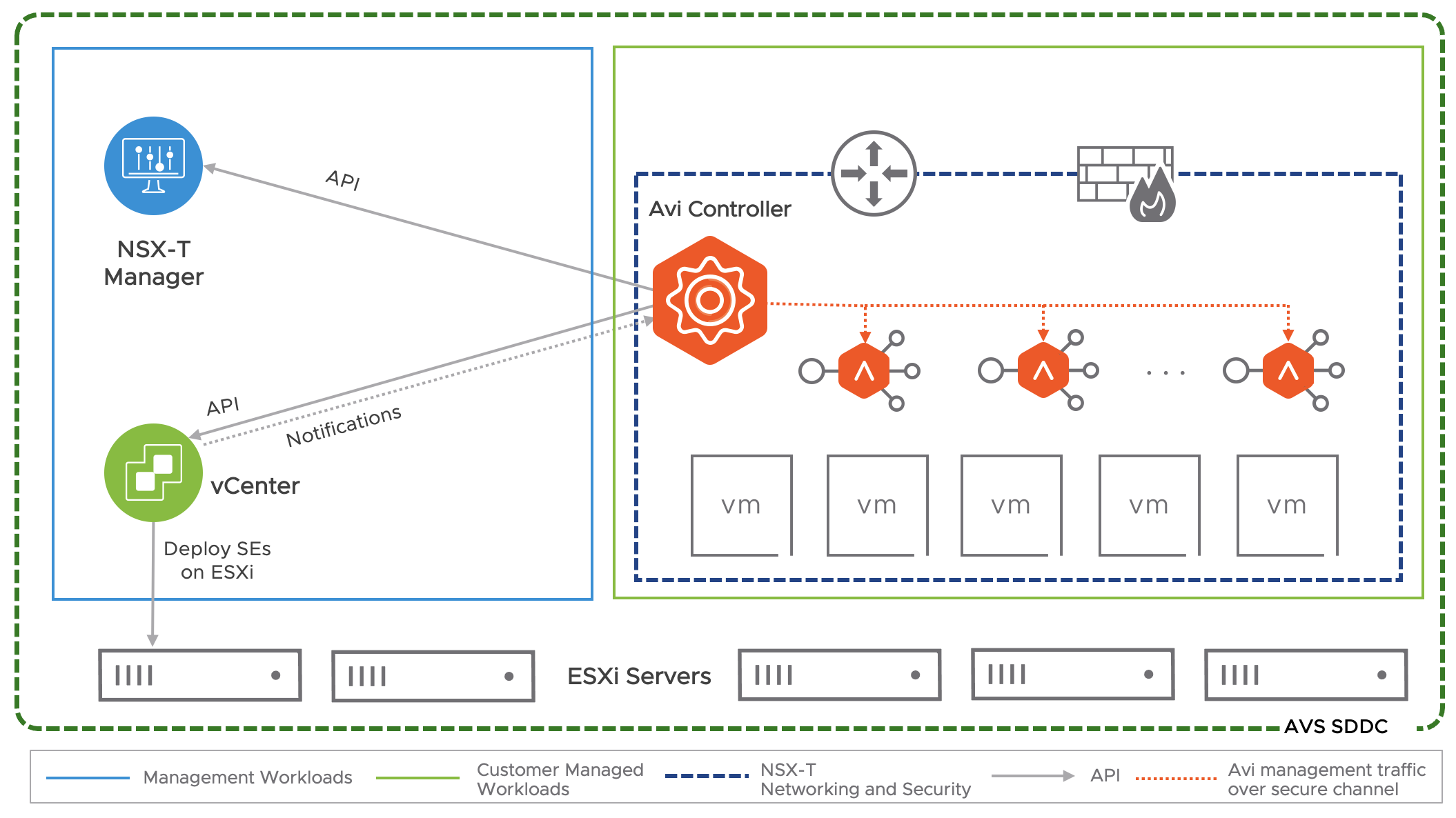
Avi provides load balancing for applications running in AVS SDDC. Avi integrates as a second party load balancing solution, with communication between the Avi Controller, NSX Manager and VMware vCenter within AVS. This integration enables Avi to deploy and manage Service Engines automatically based on demand, providing for an elastic, automated approach to load balancing.
Avi leverages the NSX-T Cloud Connector mode of operation in AVS as well. This is facilitated by the similarity in the VMware infrastructure between an on-premises NSX-T deployment as well as AVS deployment, as far as objects of interest for Avi are concerned.
Key Points from the Deployment shown above:
- The Avi Controller is a cluster of three control plane VMs. The Avi Controllers can run within the AVS SDDC, or outside it in your on-premises datacenter / Azure native VNet. The Controllers need IP reachability from the Service Engines.
- The Controller connects with the NSX-Manager and VMware vSphere vCenter within AVS and discovers the VMware objects such as Port groups, clusters, NSX T1, Segments etc.
- The Controller automatically deploys an Avi Service Engine, which is the data path instance. The Avi SE is a virtual machine running within the AVS SDDC.
- The Controller ensures that the NSX-T DFW is programmed correctly to allow traffic.
- Avi allows for various deployment configurations of the underlying NSX system, such as shared segment for the Virtual Service front-end IP (VS IP) and pool members, as well as dedicated segments for each.
- Avi also supports the default Tier 1 gateway as well as additional Tier 1 gateways created within AVS by the customer.
- While Avi supports various VLAN backed segment topologies, these are not applicable in the context of AVS as AVS supports overlay segments created by customers.
Installing Avi in AVS
Prerequisites
Licensing
- NSX Advanced load balancer only supports Enterprise Edition license for Azure VMware Solution. To know more about the Enterprise Edition license, see License Management on NSX Advanced load balancer.
- NSX ALB Licenses can be added to the Controller at any time as per the requirement. The licenses are available at my.vmware.com. Login to your account at my.vmware.com to access the VMware serial key(DLF).
- NSX ALB Controllers manage licenses and central capacity pool for NSX ALB Service Engines.
- NSX ALB allows for a 10% overage of the total license capacity.
Role Requirements
The Avi Controller requires:
- the NSX Network Engineer role or higher
- VMware vCenter permissions as defined in Roles and Permissions for vCenter and NSX-T Users
- You can use the cloudadmin user and credential provided for AVS. This user has a role which is a superset of the required permissions and is sufficient for the integration.
Content Library
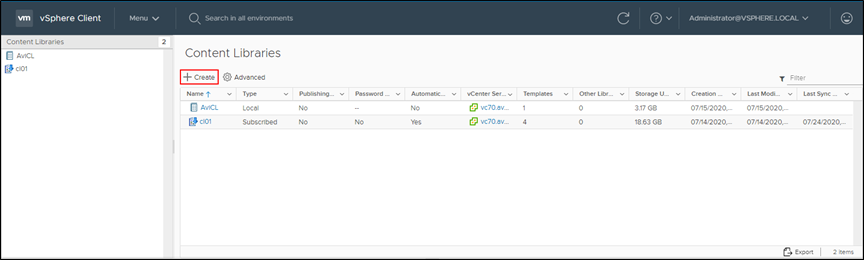
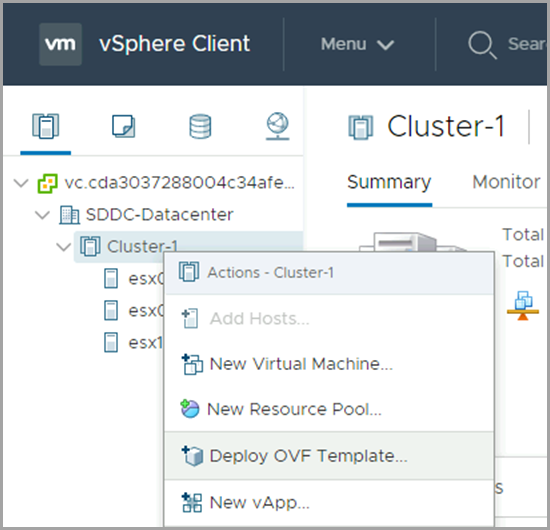
The Avi Controller uploads the Service Engine image to the content library on the vCenter server and uses this to create new virtual machine (VM) every time a new Service Engine is required. The content library must be created on vCenter before configuring the NSX-T cloud. In the vCenter vSphere client,
- Navigate to Content Libraries.
-
Click on Create.
-
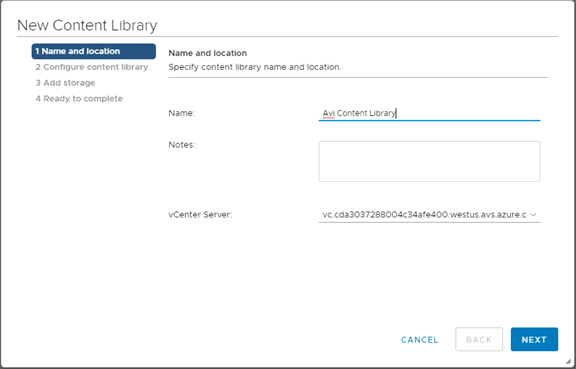
The New Content Library wizard opens. In the Name and location page, enter the Name and select a vCenter Server instance for the content library as shown below:
-
Click on Next.
-
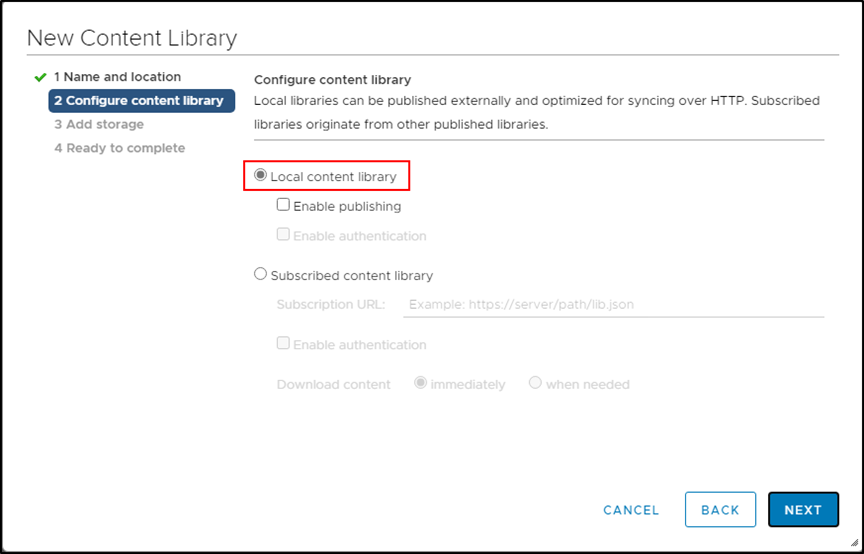
In the Configure content library page, select Local content library.
-
Click on Next.
-
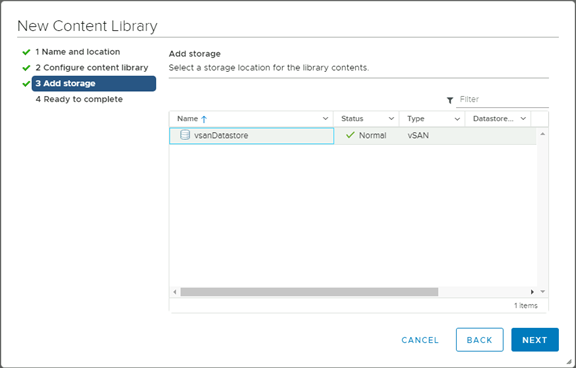
In the Add storage page, select a datastorage location for the contents of the content library.
-
Click on Next.
-
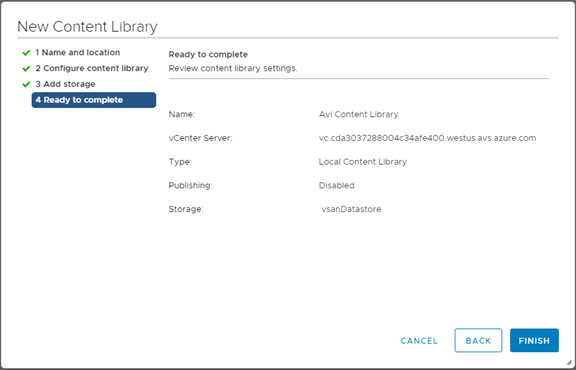
In the Ready to complete page, review the details.
- Click on Finish.
Deploying the Avi Controller OVA
To deploy the Avi Controller OVA,
-
Login to the vCenter server through a vCenter client, using the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN).
-
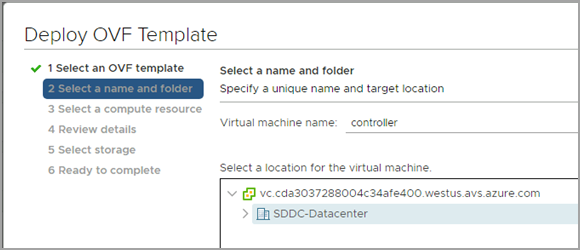
From the File menu, select Deploy OVF Template.
-
Select the
controller.ovafile from your local machine. -
In the Deploy OVF Template wizard, select the VM name and the location to deploy.
-
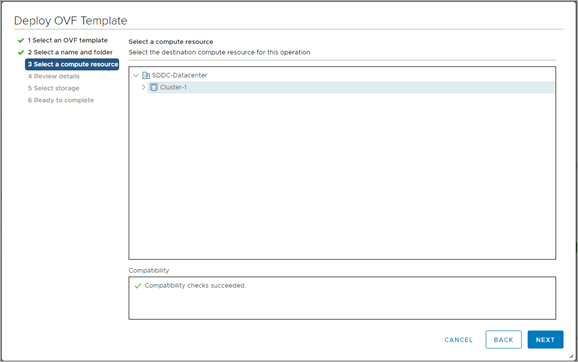
Select the compute resource.
-
Review the details.
-
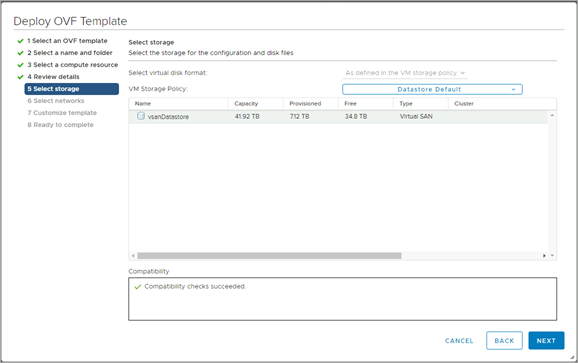
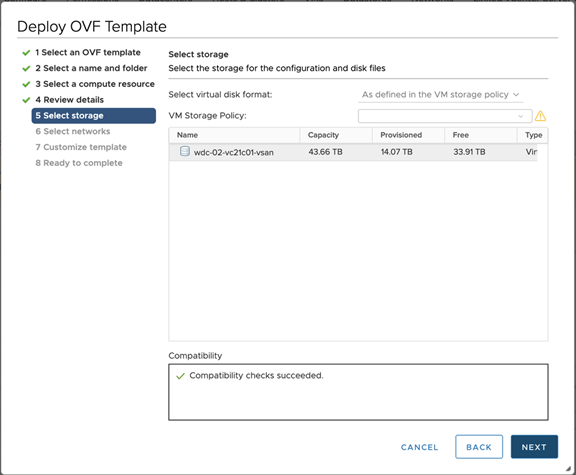
Select storage.
-
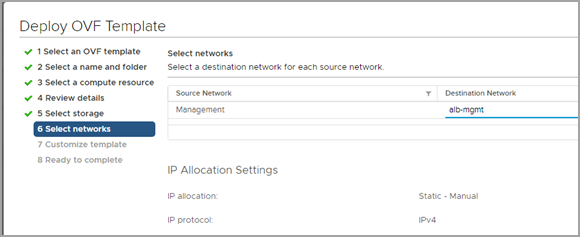
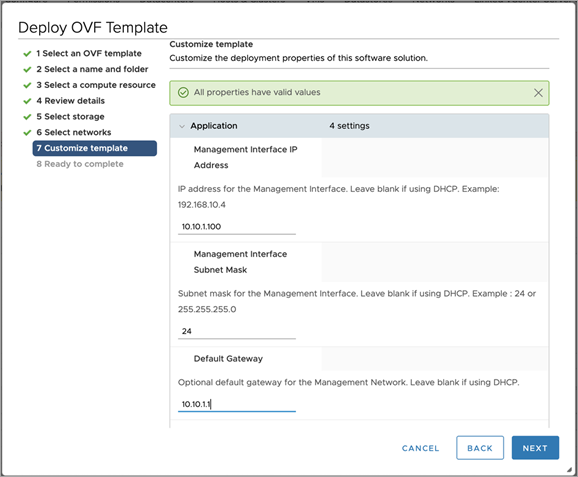
Choose a management network for the Avi Controller.
-
Enter the management IP address, subnet mask and default gateway. In the case of DHCP, leave this field empty.
Note: Using static IP address is recommended for production setups.
-
Review the settings and click on Finish.
After this, power on the virtual machine.
Setting up the Avi Controller
This section shows the steps to perform initial configuration of the Avi Controller using its deployment wizard. You can change or customize settings following initial deployment using the Avi Controller’s web interface.
-
To complete the setup, navigate to the Avi Controller IP via a browser.
Note: While the system is booting up, a 503 status code or a page with following message will appear, “Controller is not yet ready. Please try again after a couple of minutes”. Wait for about 5 to 10 minutes and refresh the page. Then follow the instructions below for the setup wizard.
-
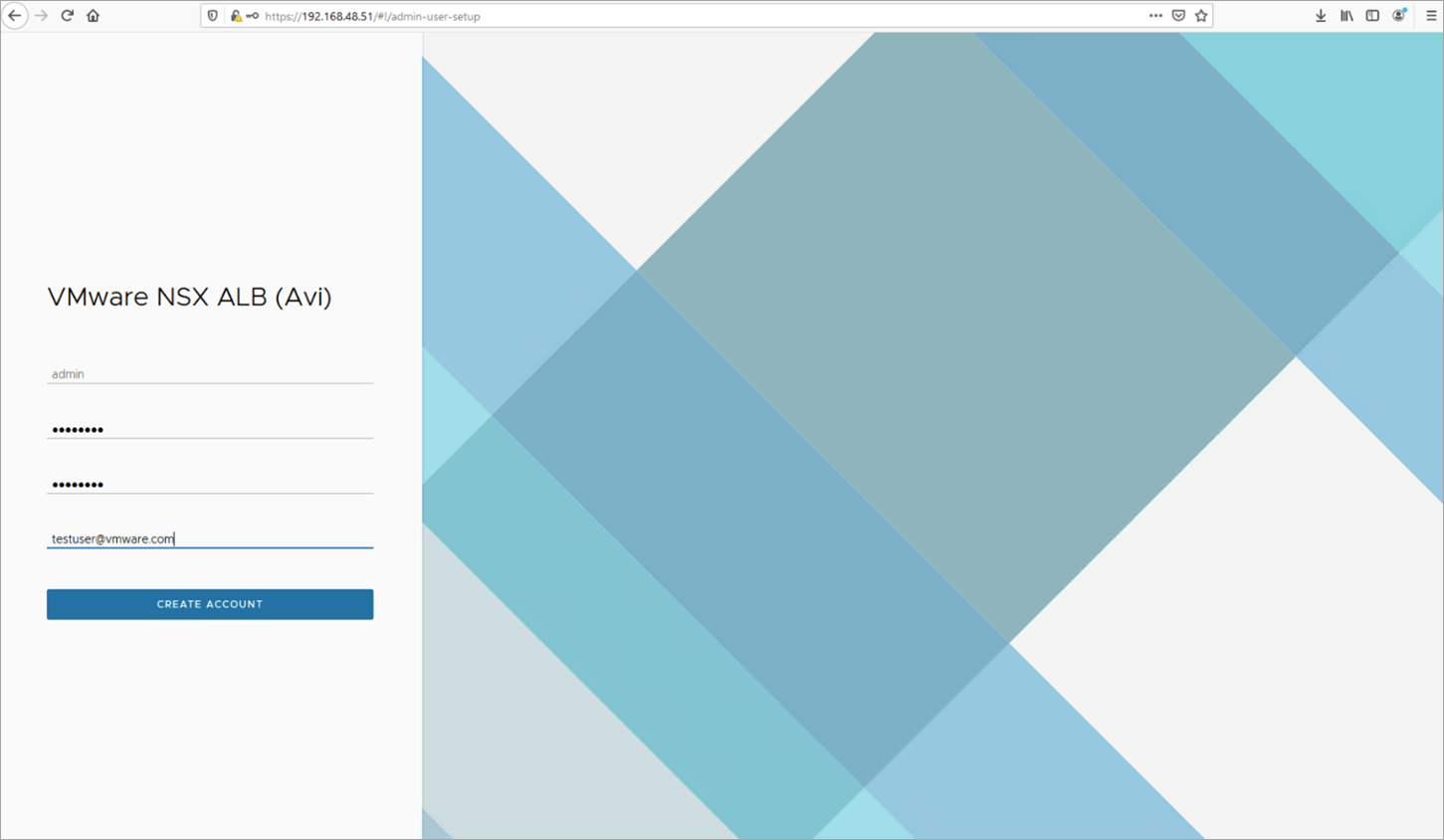
Enter the admin details as shown below:
Note: This e-mail address is required for admin password reset in case of lockout.
-
Enter the backup passphrase, DNS servr information.
-
Configure the Email/SMTP information.
-
Click on Save.
Creating an NSX-T Cloud
To create an NSX-T cloud, log in in to the Avi Controller and follow the steps given below:
Create Credentials
-
In the Avi UI, Navigate to Administration > User Credentials.
-
Click on Create.
-
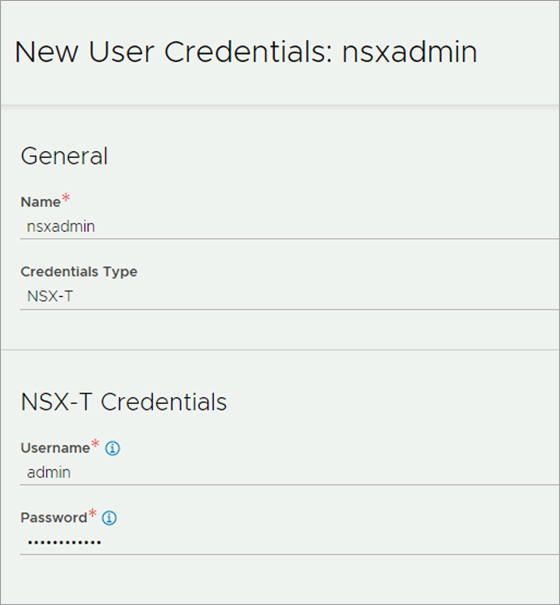
Provide a Name for the credential.
-
Select NSX-T as the Credentials Type.
-
Provide the NSX Username and Password.
-
Click on Save
Similarly, create the vCenter credentials.
Configure the Cloud
To configure the cloud,
-
Navigate to Infrastructure > Clouds.
-
Click on Create and select the NSX-T Cloud.
-
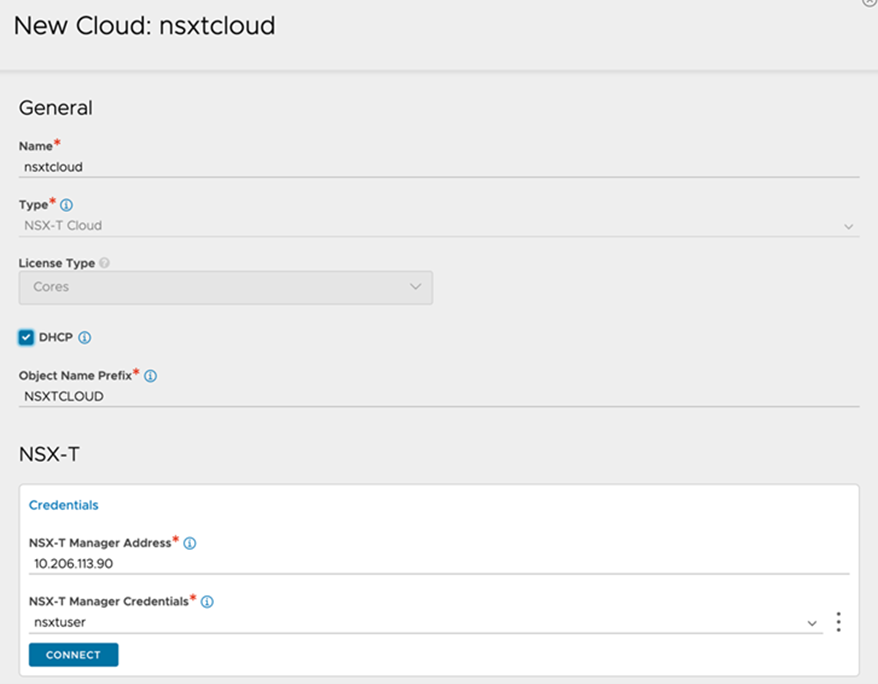
Enter the Name of the NSX-T cloud.
-
Check the DHCP option if SE management segment has DHCP enabled.
-
Enter a prefix string. The prefix string must only have letters, numbers, and underscore. This field cannot be changed once the cloud is configured.
-
Enter the NSX-T manager hostname or IP address as the NSX-T Manager Address and select the NSX-T Manager Credentials.
-
Click on Connect to to authenticate with the NSX-T manager.
-
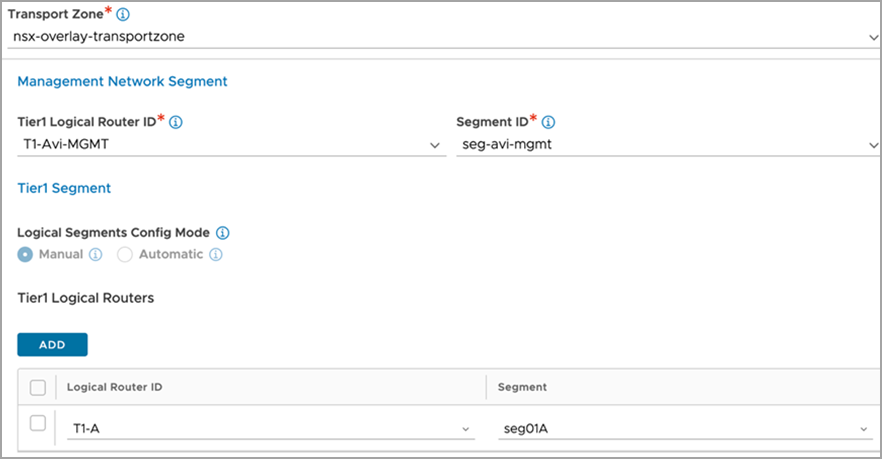
Select the Transport Zone required from the drop-down.
-
Under Management Network Segment, select the Tier1 Logical Router ID and Segment ID.
-
Select the Tier-1 gateway and logical switch for VIP placement.
-
Click on Add to select one more Tier-1 router and a connected logical segment for VIP placement.
-
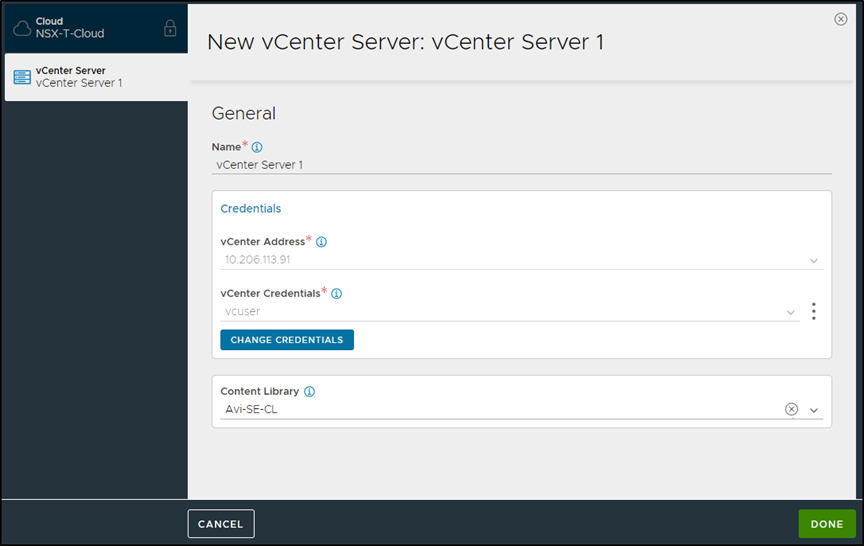
Under vCenter Servers, click on Add.
-
Enter the vCenter server Name and configure the credentials.
-
Click on Connect.
-
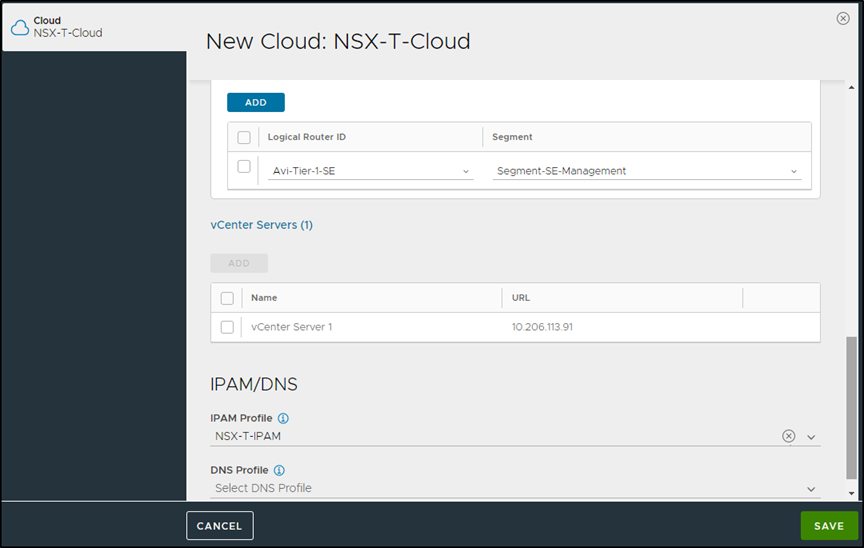
Select the Content Library and click on Done.
-
Select the IPAM/DNS Profile, as required.
-
Click on Save to create the NSX-T cloud.
The Cloud Connector Status will turn green, and the system is ready for creation of a Virtual Service.
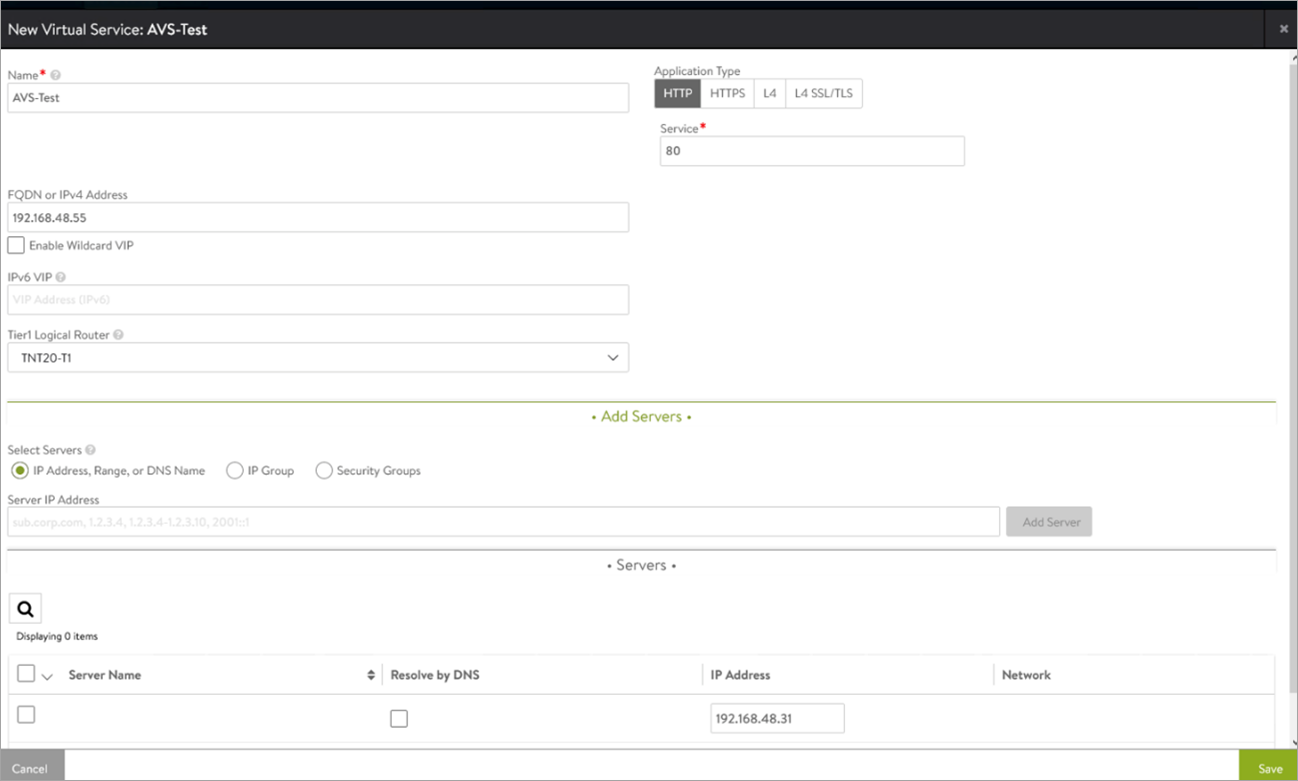
Creating a Virtual Service
-
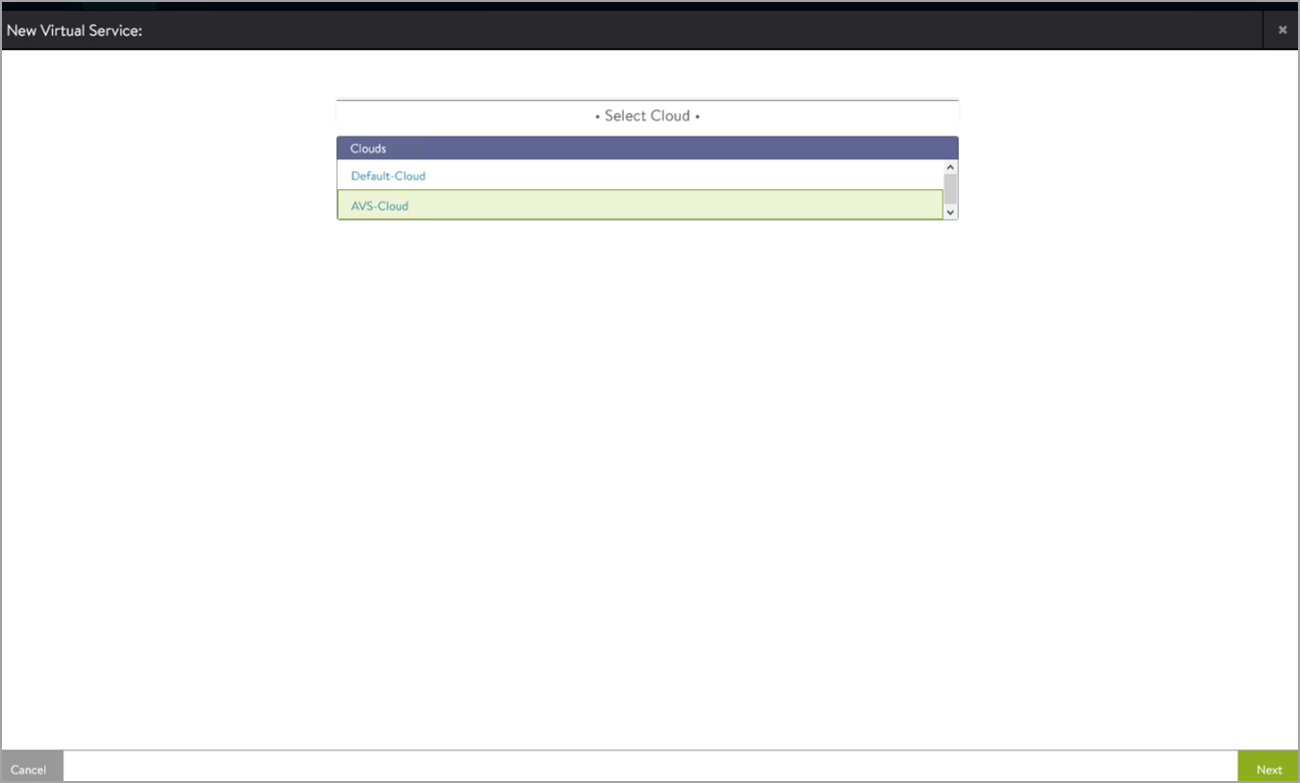
From the Controller UI, navigate to Applications > Create Virtual Service (Basic Setup).
-
Select the cloud.
-
Enter the details related to the VS IP, Pool members, Tier 1 Logical Router, etc.
-
click on Save to create the virtual service.
On successful creation of a Service Engine, the virtual service will come up and will be ready to process traffic.
Document Revision History
| Date | Change Summary |
|---|---|
| July 09, 2021 | Published the Installation Guide for VMware NSX ALB for AVS |