Network Monitoring Definition
Network Monitoring, a subset of network management, is a systematic attempt by a computer network to identify slow or failing components before they cause problems. For example, crashed, frozen, or overloaded servers; failed switches; failing routers; and other troublesome components can all potentially cause outages or network failures. Should some problem arise and trigger an outage, it is the role of the network monitoring system to alert the network administrator in a timely way.
Typically, administrators monitor and manage a network using network monitoring tools and software applications. These network monitoring services help users monitor performance, and detect whether a web server is properly connected to worldwide networks and functioning as expected. In fact, many network performance monitoring tools also offer an end-to-end visualization of the networks and the applications.
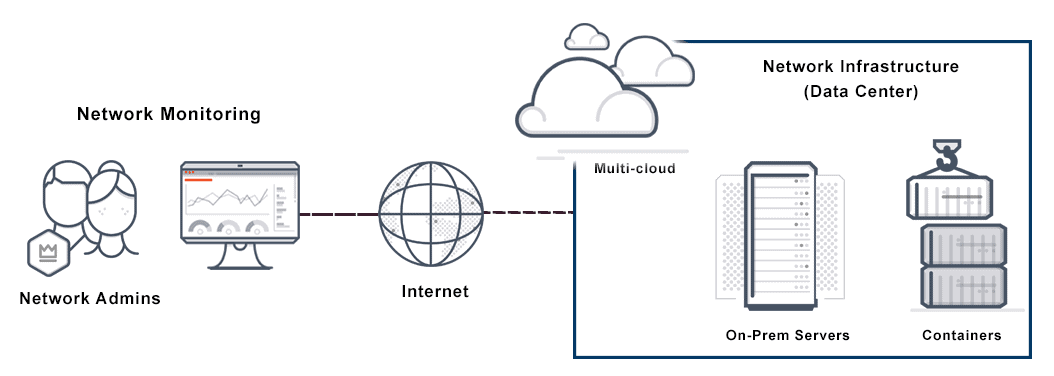
How Does a Network Traffic Monitoring System Work?
The first step of effective network monitoring is identifying the devices to be monitored and their related performance metrics. The next step is selecting an appropriate monitoring interval.
Routers, servers, and switches perform business-critical tasks, so these components demand more frequent monitoring. In other words, internet traffic monitoring intervals rely upon particular parameters and usage and should be selected based on the facts of a specific situation. The best systems allow users to create customized alerts.
A network monitoring design should cover every aspect of IT infrastructure, such as the connectivity, network, and security systems. It should ideally include a single-pane-of-glass view into the network, allow administrators to monitor devices seamlessly, and offer network maintenance, problem detection, reporting, and resolution.
Every web traffic monitoring system should also offer reports for a range of users, including systems administrators, network administrators, and IT management. Finally, a secure network monitoring system should be user-friendly, and offer basic drill down and reporting functionalities.
What Does a Network Monitoring Tool Do?
Network monitoring tools and systems constantly monitor a network’s health and reliability by tracking and logging network parameters and searching for trends. A network monitoring system will watch and compare data transmission rates (throughput), uptime/downtime rates, error rates, response times to inputs and requests (both user-generated and automated), and use-time percentages to parameter thresholds that users set in advance. When levels reach those thresholds, the network monitoring system triggers an alarm and initiates network fault management processes.
There is more than one way network traffic monitoring tools as part of a network monitoring system might alert administrators to performance and security problems that can harm the network. Triggers are events that will generate alarms in the system. An event might refer to a deviation from mean value of a parameter, a crossed threshold parameter value, a change in the state of a node.
Threshold violations generate most alerts, but users can also set a network activity monitor to generate alerts based on time delays or repeat count of threshold violations. For example, a network monitoring and maintenance system can be configured not to generate an alert if a threshold is breached—until it is breached twice in 15 minutes. Similarly, an alert can be generated after an initial threshold violation returns to its baseline value or resets.
Certain threshold violations may be expected. Users may configure a network usage monitor to suppress these types of alerts. In other situations, the same sort of facts may cause multiple threshold violation alerts. Monitoring systems that support deduplication of alerts or consolidation of alerts can eliminate this problem.
How Do Secure Network Monitoring Tools Work?
Ping is a basic network monitoring tool that tests host availability and reachability in an IP network. Ping results data can determine whether a network host is active, or measure the packet loss and transmission time while communicating with a host.
Other common network performance monitoring tools monitor performance at the enterprise network level. Network monitoring systems deploy internet traffic monitoring tools such as mail server (POP3 server) monitoring and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) monitoring applications.
What is Network Performance Management?
Network performance management refers to the total body of techniques used to manage performance across a computer network. The network performance management process demands continuous monitoring of mission critical network performance management functions and metrics.
Application network performance management tools include network connectivity monitoring tools in particular, as well as traffic monitoring systems more generally.
What is Network Monitoring Software?
Some organizations use multiple network monitoring solutions including web traffic monitoring software to manage and monitor their network operations. This can sometimes mean that when there is a problem, it takes using several of these tools, including data, graphs, and reports, to uncover the real source of the problem.
Using integrated network management software allows some users to avoid this issue. This kind of network monitoring service offers cloud based network monitoring in real-time and provides more detailed insights into the issues that are slowing down the network. This in turn enables quicker fixes and less downtime.
The right network monitor software depends on your organization, so any package, whether it is a free version or a more premium offering, should offer targeted capabilities and scalability. Remote network monitoring solutions such as those that are software- or cloud-based offer the benefits of internal network monitoring without the need for a network monitoring server.
Availability Monitoring vs Interface Monitoring vs Server Monitoring
Availability monitoring simply refers to the totality of hardware, IT infrastructure, software, network monitoring tools, and other solutions an organization uses to ensure that its resources are available to meet its business needs. Monitoring and managing IP addresses and network connections constantly helps ensure high levels of network resource availability.
This is a continuous monitoring process that helps protect bandwidth availability, storage space, and application functionalities. Availability monitoring includes traffic monitoring and analysis, but it is not limited to that type of monitoring.
Any given network uses various kinds of interfaces, such as Gigabit Ethernet and Fast Ethernet, or very high-speed Fiber channel interfaces. Any interface is the entry and exit point on a device for packets—each of which provides a service.
Poor user experience can result from any packet loss, discards, errors, utilization limits, or of course downtime on the part of the interface. Interface monitoring and sometimes network speed monitoring watch for these kinds of issues and offer alerting and reporting options when there are problems.
Server monitoring is part of what network monitoring systems do as they gather interface statistics from network devices with SNMP or ping.
What is a Throughput Monitor?
Network throughput refers to how much data a given network transmits over a set time period. For instance, an Ethernet connection that transfers data at a rate of 40 Megabits per second has a 40 Mbps throughput.
Network throughput monitoring or throughput monitoring protects these high speed transmission rates. Application throughput monitoring focuses on the throughput speed of a specific application.
Does Avi offer a Real Time Network Monitoring Solution?
Avi is a smart, software-defined load balancer, but it does far more. Its features include multi-cloud traffic management, real time traffic monitoring, application performance monitoring (APM), security, predictive autoscaling, and container services.
Avi’s elastic load balancing solution can do many of the same things a dedicated APM tool does, including shrinking rollout times for applications and new services, minimizing delays. The platform also provides rapid incident resolution, allowing users to see system-wide views at-a-glance, monitor the health of applications, and map interactions visually.
Learn more about the benefits of Avi’s elastic load balancer as a cloud based network monitoring solution here: APM Tools | Network Monitoring Simplified by Avi Networks.
For more on the actual implementation of load balancing, security applications and web application firewalls check out our Application Delivery How-To Videos.